Guava Tree - White
View More Planting Info
Choose a position in full sun with 20 feet of space between plants and buildings. The soil must be well-draining and at a pH between 5 and 7. They are not fussy regarding soil type as long as there is enough drainage. Dig a hole twice as wide and at the same depth as the rootball, remove the tree from its container, and gently loosen the roots before placing it in the hole. Backfill with soil tamping down to remove air pockets. Make a basin around the base to catch any rainfall and water the roots thoroughly. Add a layer of mulch, being careful not to touch the tree trunk to regulate the temperature and conserve water. When planting in containers, choose large pots at least 20 – 24 inches in diameter. Fill with good potting soil and make sure it has enough drainage holes. Plants potted in this way will grow more compact, 8 feet tall and 3 feet wide.
Harvesting:
Harvest fruit in summer when they are yellow but still firm. They should have a tropical guava aroma.
Pruning:
Prune to maintain the shape of the trees and remove any diseased or damaged branches.
Growth:
White Guava Trees grow 20 feet in-ground and less than 10 feet in containers. Plant 20 feet away from other plants
- Product Info
- Care and Maintenance
- Planting Care
- Growing Zone
Product Info
Mature Height: 8 ft. in Container
Mature Width: 3 ft. in Container
Sunlight: Full Sun
Growth Rate: Moderate
Does Not Ship To: AZ, OR
Care and Maintenance
Watering: Water guava trees twice a week after planting to get them established. Containers may have to be watered more frequently, especially during warmer weather. They like consistently moist soil but it should not become waterlogged.
Fertilizing: Guava trees are heavy feeders but only need feeding three to four times a year when established. For the best results, use a formula high in nitrogen, phosphoric acid, and potash. Extra magnesium will keep them healthy. When first planting, feed the trees every 1 to 2 months until established. Use a slow-release fertilizer and follow the manufacturer's instructions.
Pruning: Prune to shape the trees and allow light to penetrate the center of the canopy. Guava fruits on new growth, so pruning will not adversely affect fruit production. Remove any diseased or damaged branches and any that are crossing, which could rub together in a breeze and cause damage and invite diseases.
Pests and Diseases: These trees are not affected by many pests and diseases but look out for scale insects, mealy bugs, flies, moths, thrips, and red spider mites. Treat pest issues with insecticidal soap or neem oil.
Pollination: White guavas are self-pollinating but having a second guava tree nearby can improve fruit set. Bees and butterflies are attracted by the fragrant white flowers in spring.
Harvesting: Harvest fruit in summer when they have yellowed in color but are still firm. They should have a sweet tropical guava aroma.
Recovery Time: Transitioning from our nursery to your home can be a bit of a shock to your plant. A short acclimation period helps it recover and reduces stress.
Climate Adjustment: Every environment is unique. Giving your plant time to adjust to the local climate, humidity, and light conditions in a shady spot will set it up for better growth and health.
How to Acclimate Your Plant: Keep the plant in its container and place it in a shady, sheltered area away from high winds. Ensure it's watered adequately – the soil should be moist but not waterlogged. Monitor the plant for any signs of distress and allow it to adjust for a few days before planting. After a few days of acclimation, your plant will be better prepared to thrive in its new home for years to come.
Planting Care
Sunlight: Plant in full sun.
Soil: Plant in well-draining soil with a neutral to slightly acidic pH between 5 and 7.
Mature size: Trees planted in the garden will grow 15-20 feet tall and 10-20 feet wide. Container plants will be limited by their pot size.
Climate: Although tropical in nature, this guava will withstand temperatures down to 30°F (-1°C). It can be grown in a wide range of climates and can be grown in containers to be moved out of extreme weather.
Thinning: Thin after the trees have fruited to get more light into the canopy of the tree and to shape it.
Location: These trees need plenty of open space and a sunny position in the garden.
Watering: Once established in the ground, the tree will be relatively drought-tolerant, but water at least weekly during its first year of growth and then gradually taper off. Plants in containers must be watered year-round. Keep the soil evenly moist but not soggy.
Pruning: Prune to maintain the shape of the trees and remove any diseased or damaged branches.
Spacing: Plant at least 20 feet away from other trees or nearby structures in your garden.
Harvesting: Harvest in summer when the fruits are aromatic and just soft.
Pollination: White guava is self-pollinating and does not require a second guava for pollination, but may have improved yields if one is provided. Container plants may need hand pollination to set fruit.
Hardiness Zone: The White Guava Tree is suitable for planting in USDA zones 8-11. In zones outside of its normal range, plant in a container that can be brought into a warmer location to overwinter.
Fertilizer: Feed 3 times a year in spring, summer, and fall. Avoid feeding in winter. Use a slow-release formula high in nitrogen, potassium, and phosphorus with added magnesium.
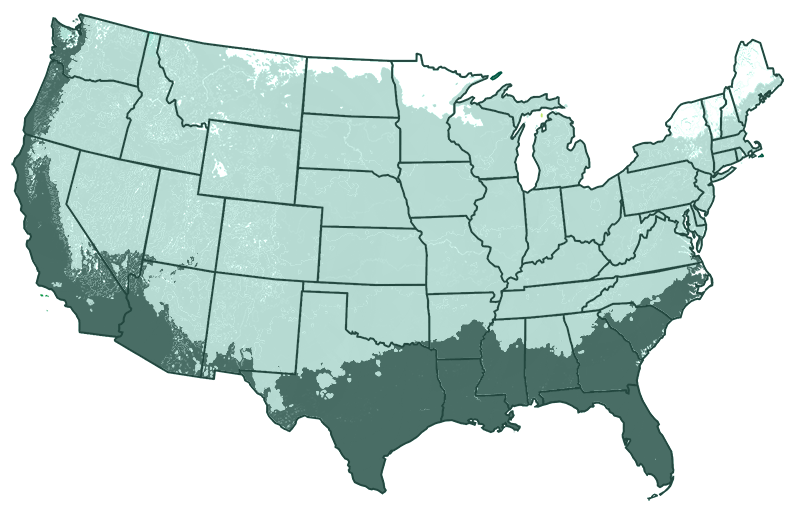
Growing Zone
Grows Well In Zones: 4-11 patio / 8-11 outdoors